In this guide, we’ll walk you through how to build a memory agent that can learn, store, and reuse skills, just like how humans develop habits. These skills will be modeled as neural modules, allowing the agent to build procedural memory by recording actions, tracking context, and recalling learned behaviors when encountering similar situations.
By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of how to create an agent that continually learns and adapts, becoming more efficient with every interaction.
Whether you’re just getting started or looking to expand your knowledge of AI agents, this step-by-step guide will give you the tools to build a solid, scalable framework for skill learning. Let’s explore how to bring this concept to life through code.
Representing and Storing Skills
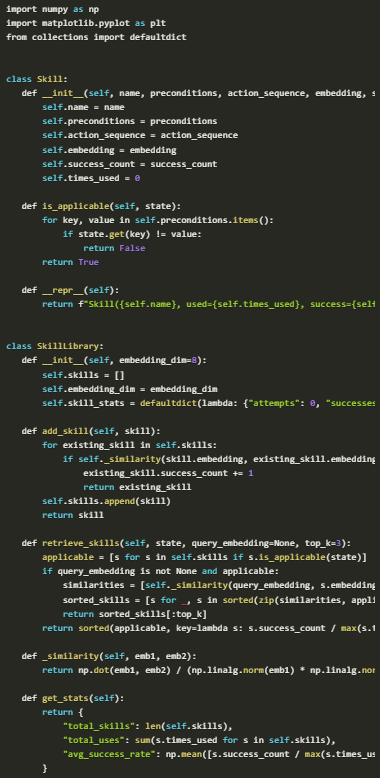
Here, each skill is tagged with key details such as metadata, embeddings, and usage stats, making it easier for the agent to recognize when a skill can be reused. By using cosine similarity, the agent can compare new situations to past experiences and match them with the most relevant skills.
This process of similarity-based retrieval helps the agent learn from its previous actions, making it more efficient and capable of performing tasks based on what it already knows.
Building a Learning Environment

In this step, we create a simple environment where the agent can learn basic tasks, like picking up an object, unlocking a door, and reaching a target. Think of this as a controlled “playground” where the agent can practice and develop its skills.
The goal here is to observe how simple, basic actions like moving or interacting with objects transform into more complex, repeatable skills as the agent interacts with its environment over time.
By running multiple episodes, we can easily see how the agent’s behavior improves: it becomes more efficient, using previously learned actions to complete tasks faster and more effectively. The environment is structured to easily track these improvements, so we can understand exactly how the agent is learning and progressing from one episode to the next.
Building Contextual Embeddings for Skill Reuse
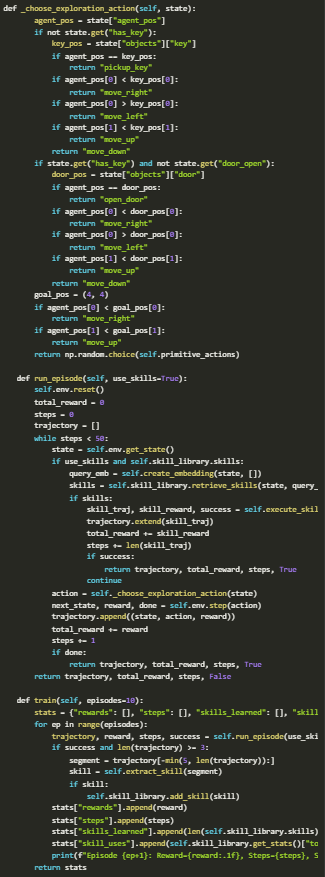
We start by building embeddings that capture the context of each state-action sequence, making it easier to compare and reuse skills. By extracting skills from successful trajectories, we transform raw experiences into actionable, repeatable behaviors.
As we run the code, we can observe how simple, exploratory actions slowly evolve into structured knowledge. The agent learns to identify patterns and apply them in future situations.
Over time, exploration transitions into more targeted, efficient behaviors, allowing the agent to reuse these skills effectively as its experience grows, thereby improving its decision-making.
Balancing Skill Reuse and Exploration

In this step, we define how the agent decides between reusing known skills and exploring with basic actions. By training the agent over multiple episodes, we track how learned skills, usage frequency, and success rates change.
Through this process, we notice that as skill reuse increases, the agent’s performance improves: episode length decreases, and overall rewards increase.
The balance between exploration and skill reuse is key to the agent’s development, allowing it to use previously learned behaviors to accelerate progress while still experimenting with new actions when necessary.
Visualizing the Growth of Learned Skills
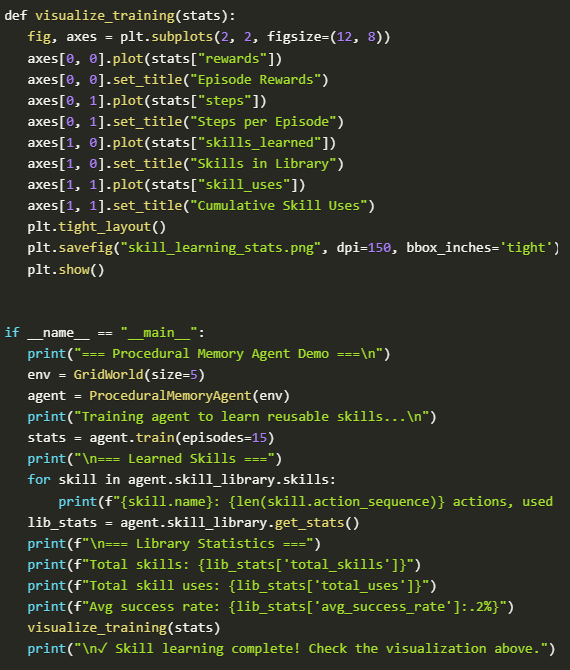
Finally, we bring everything together by running training and displaying the learned skills and behavior statistics. We plot the trend in rewards and observe how the skill library grows over time, providing a visual representation of the agent’s learning journey. As the agent completes more episodes, we see its ability to make smarter, faster decisions improve significantly.
The skill library expands as the agent reuses and refines its knowledge, becoming more intelligent and efficient with experience. This marks the completion of the procedural memory formation lifecycle, demonstrating the agent’s evolution into a more capable problem-solver.
Evaluating the Performance of a Memory Agent
Measuring Task Efficiency and Completion Time
To evaluate a memory agent’s performance, task efficiency is key. We measure how quickly the agent completes assigned tasks, focusing on how effectively it uses learned skills. The goal is to assess if the agent is optimizing its actions based on previous experience, rather than starting from scratch each time.
Monitoring completion time allows us to track the agent’s progress. Ideally, as it learns, it should complete tasks faster. This is a direct measure of how effectively the agent’s procedural memory is functioning, leading to more efficient decision-making over time.
Assessing Skill Reuse and Adaptability
A strong memory agent should not only learn new skills but also effectively reuse them in different scenarios. By assessing skill reuse, we can determine how well the agent applies past knowledge to solve new problems. This involves tracking how often previously learned skills are successfully recalled and applied in similar contexts.
Adaptability is also crucial: the agent must show it can adapt those skills to handle slightly different situations. Evaluating this helps ensure the agent isn’t just memorizing tasks but is learning to generalize its knowledge and apply it flexibly.
Tracking Success Rates Across Episodes
By tracking how often the agent successfully completes tasks across multiple episodes, we can assess its growth and the effectiveness of its memory system. Over time, we should see an improvement in the agent’s success rate, reflecting its ability to apply learned skills efficiently.
This metric also highlights areas where the agent may still be struggling, allowing us to refine its training and skill set. A rising success rate suggests the agent is becoming more reliable and proficient in its tasks.
Evaluating Memory Retention and Recall Accuracy
Memory retention and recall are central to a memory agent’s performance. To evaluate this, we assess how well the agent remembers and retrieves skills over time, especially when faced with unfamiliar but similar situations. The agent should be able to recall relevant skills from its memory and apply them accurately, even if the environment or task changes slightly.
Evaluating recall accuracy helps us identify whether the agent is retaining essential information or forgetting key skills. A high recall rate indicates that the agent has a strong memory system capable of effective knowledge retention.
Analyzing Reward Optimization and Behavior Improvements
Reward optimization is another important factor in evaluating a memory agent’s performance. We measure how well the agent optimizes its actions to maximize rewards over time, ensuring it learns to prioritize the most beneficial behaviors.
If the agent consistently improves its actions and increases rewards, it shows that its learning system is effective and evolving. Analyzing these improvements provides insights into how the agent is progressing and adjusting its behaviors to achieve better outcomes.
Bottom Line
To sum up, we see how procedural memory develops as the agent learns to extract skills from its own successful experiences. We watch as these skills take shape, with structure, metadata, embeddings, and usage patterns that enable the agent to reuse them effectively in future scenarios.
What’s exciting is how even a simple environment and basic rules can create significant learning dynamics. This gives us a clear, practical sense of how an agent gradually builds and refines reusable skills over time, ultimately improving its ability to perform tasks more efficiently as it learns.
Looking to supercharge your business with AI that actually works for you? Imagine having a custom GPT or AI solution that doesn’t just look good on paper but helps you solve real problems, make smarter decisions, and streamline your workflow. At Techling, we specialize in delivering practical, impactful services like AI answering, custom software development, data analytics, machine learning, MVPs, LLM development, and much more.
We don’t just offer tools, we offer a roadmap to unlock the full potential of AI for your business. Ready to transform your processes and open new doors of opportunity? Techling is here to guide you.
FAQs
Neural modules are structured components of a memory agent that store, process, and retrieve learned skills. These modules allow the agent to build procedural memory, making it capable of applying previously acquired skills to new situations.
The memory agent learns new skills by interacting with its environment and completing tasks. Successful task completion leads to the formation of reusable skills, which are stored in the agent's neural modules for future use in similar scenarios.
Contextual embeddings are used to capture and retain important context during skill learning. They allow the agent to understand the context in which a skill was used and ensure the skill is applied appropriately when similar situations arise.
Skill reuse allows the agent to leverage previously learned actions in new tasks, improving its efficiency. By reapplying past experiences, the agent can complete tasks faster and more accurately, reducing the need for constant exploration.